
DNA extraction from saliva has become increasingly popular in recent years. Saliva collection is safe and non-invasive, and saliva collection kits can be mailed to donors for self-collection at home.
DNA or RNA can be isolated from the donor or their oral microbiome and used for many applications, such as investigating infectious diseases, cancer, ancestry, population studies, genotyping, and gene expression studies.
Traditionally, challenges with saliva samples included microbial contamination and lower nucleic acid yields. However, there have been significant improvements in devices to collect saliva, and good yields of high quality can now be extracted[i].
Many collection, stabilization, and isolation methods are available, and variations in sample collection and handling can dramatically affect data quality. This article gives ten tips for sample collection, handling, and storage, to ensure you get the best results from your samples and avoid wasting time and money.
The saliva DNA/RNA collection and extraction workflow has the following stages:
1. Determine the nucleic acid purity required for your analyses
The first step in planning your saliva collection strategy is to determine the purity of nucleic acids you need for your analyses. If it isn’t required, there is no need to spend time and money obtaining high purity DNA or RNA.
Sensitive downstream applications such as rt-qPCR and Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) require high-purity RNA (A260/280 ratio of >1.9) and DNA (A260/280 ratio of ~1.8). However, if a less sensitive technique, such as PCR, is to be used, then a rapid sample preparation method, such as a direct-to-PCR kit, can provide a faster and more cost-effective alternative to a conventional multi-step purification method.
A secondary isolation step can be used for DNA for sensitive applications if samples are contaminated due to poor sampling techniques or non-optimized DNA isolation kits.
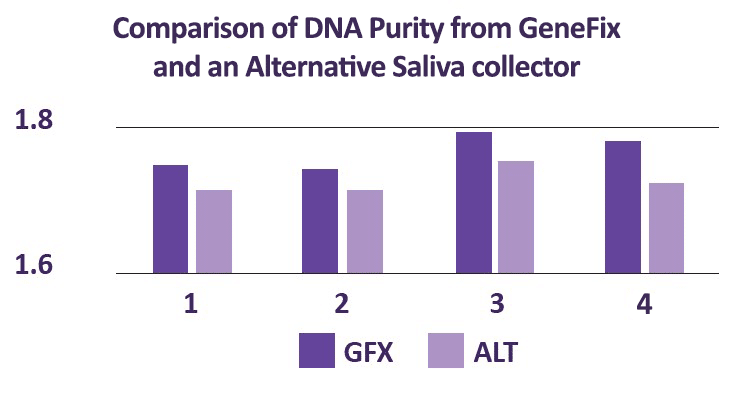
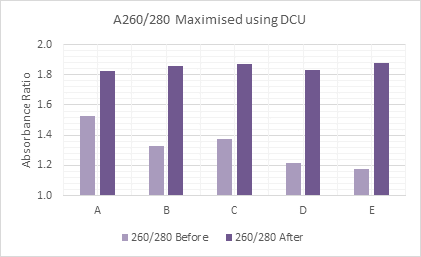
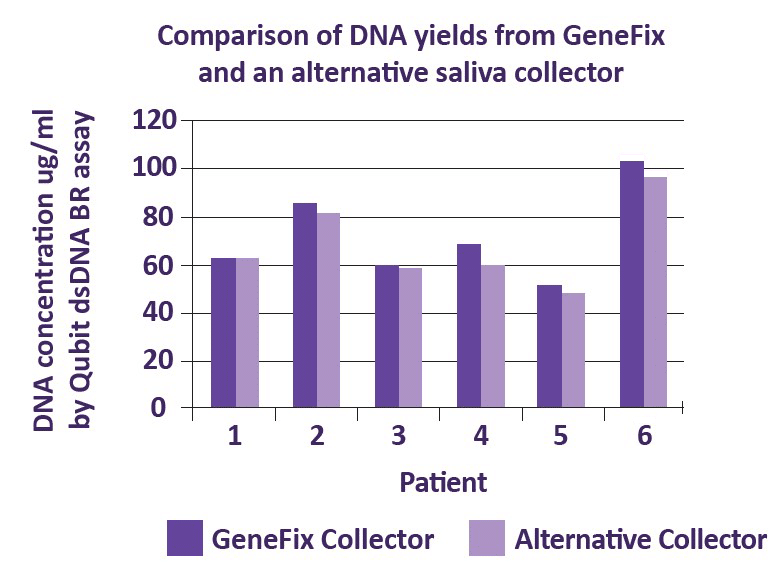
2. Consider sample yields
As with sample purity, the required yield will depend on your downstream analyses. If you plan to store samples and revisit them for future studies, you may need higher yields of nucleic acids.
How much DNA is in saliva?
Originally, collection devices were designed to collect 1ml or 2ml saliva, but newer devices eg GFX-03, can collect up to 3ml, if higher yields (300μg+) are required, e.g., for biobanking. Collection devices for larger volumes of saliva include higher concentrations of stabilization buffer to allow for dilution by extra saliva.
3. Make collection simple
Some donors, e.g. children or elderly patients, can find it difficult to produce saliva. Saliva production can be stimulated by gently rubbing the cheeks, or a kit including absorbent swabs to assist with collection, such as GFXA-01 can help.
Instructions for use must be clear, particularly if saliva is to be collected remotely without specialist supervision. Clear, legible markings on GeneFix™ collection tubes indicate the correct volume of saliva to be delivered, and donors need to ensure that they don’t include bubbles when measuring the liquid level in the tube.
Saliva collection process: A simple to attach funnel makes it easy to collect saliva in a tube prefilled with stabilization reagent for transport and storage of the sample.
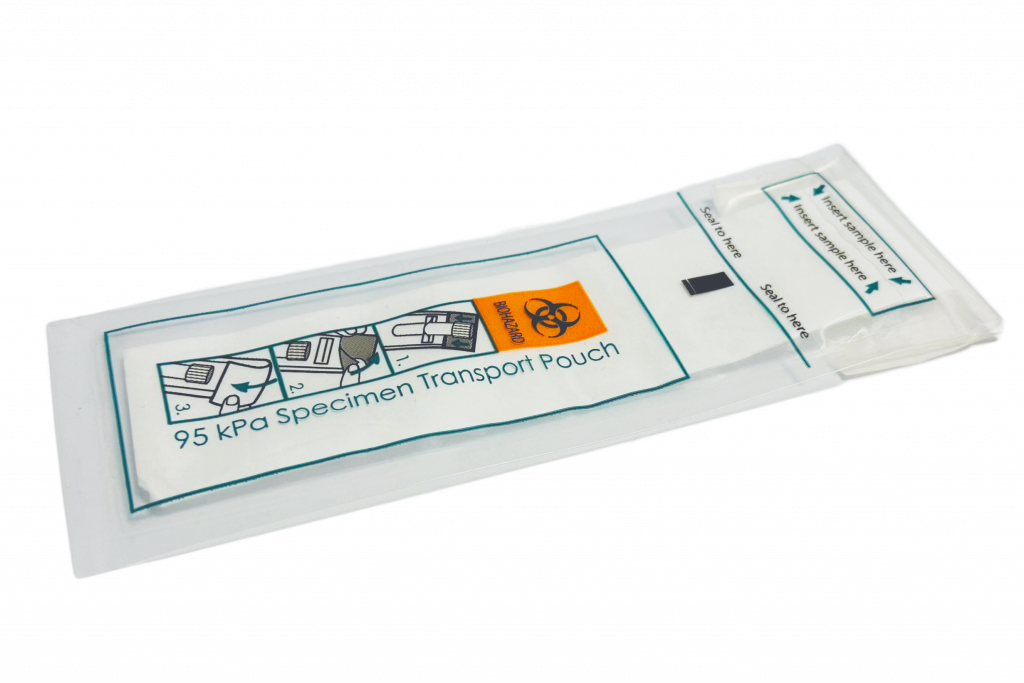

4. Use transport packs and stabilization reagent
One of the key benefits of using saliva rather than blood as a source of nucleic acids is that samples can be collected remotely and mailed for analysis. If a stabilization reagent is included in the collection tube, keeping samples cold is not required, significantly reducing costs and logistical challenges associated with storage and transport. However, collection tubes must be manufactured from robust materials that can withstand the rigours of the mailing process – regulations on leak-proof sample transport specify that collection tubes must withstand defined physical pressures of 95KPA.
IsohelixTM TPS-50 transport packs are pressure tested and include secure sealing strips and absorbent material that retains samples leaking from the primary tube within further layers of packaging.
5. Automate analysis for large numbers of samples
If large numbers of samples are to be analysed, automating your nucleic acid extraction workflow will significantly speed up the process and reduce hands-on time. Collection kits are available with 1D and 2D bar codes for tracking large numbers of samples.
If you are using instruments, select a tube that fits your instruments and racking systems. Collection kits designed for high throughput workflows (Isohelix GFXH range) have tubes with locking bases and caps that can be auto de-capped.

6. Prevent sample contamination by avoiding food and drink before collection
To prevent sample contamination it is good practice to ensure that donors do not eat, drink, smoke, or chew gum for at least 30 minutes before providing a sample.
Contaminating microbial DNA in human saliva can alter the detection of variants from whole genome sequencing, but this problem can be reduced by using a bacterial decoy in the alignment process[ii].
7. Preserve samples with collection kits including stabilization buffer
You may want to extract and analyse the nucleic acids from your samples immediately, or you may prefer to process partial samples and preserve the remainder for future testing. There are kits available for processing variable sample volumes, which work well for biobanking, when samples are stored for long periods.
How long can saliva DNA last?
GeneFix saliva collection kits are able to keep DNA stabilized at room temperature for 5 years and RNA stabilized for 2 months. For long term storage, GeneFix kits are also suitable for freezing at temperatures down to -80°C.
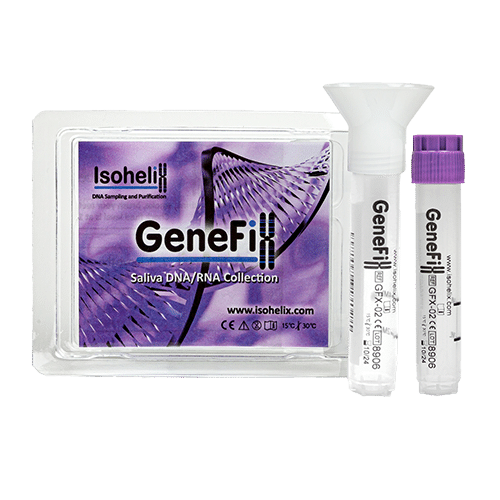

8. Avoid using hazardous reagents
Your collection and stabilization kit should be free from toxic reagents such as guanidium, for safe use in the field and for shipping and handling. GeneFixTM devices are completely non-hazardous, non-toxic and chemically unreactive, as well as including a novel funnel design which prevents sample spillages and flow back, even if the tube is knocked over.
9. Preserve microbial profiles for microbiome studies
Stabilization reagents that preserve microbial DNA at room temperature for at least a year are available (eg MFX-01). Stabilization is instant, and the buffer prevents bacterial growth, ensuring the sample accurately reflects the oral microbiome at the moment of sampling. If you are analysing microbial DNA, the devices and buffers you use must be free from any traces of contaminating bacterial DNA.


10. Make sure to use high-quality kits
Use kits manufacture to recognised quality standards for safe use and high-quality nucleic acid isolation. Isohelix has ISO 9001, and ISO 13485 accreditation, and GeneFix products are CE/IVD and UKCA marked to ensure your samples are collected, transported, and stored securely and can be used to generate excellent results.
References
[i] Hughes, S.R., Chapleau, R.R. Comparing DNA quantity and quality using saliva collection following food and beverage consumption. BMC Res Notes 12, 165 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-019-4211-6
[ii] Samson, C.A., Whitford, W., Snell, R.G. et al. Contaminating DNA in human saliva alters the detection of variants from whole genome sequencing. Sci Rep 10, 19255 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-76022-4
Saliva Collection
DNA/RNA Saliva Collection Kits
Full range of high-quality collection and stabilzation devices for saliva samples
Saliva Extraction
DNA/RNA Saliva Extraction Kits
Wide range of isolation/purification kits optimized for saliva samples


 Email Us
Email Us