The quality of DNA samples affects the quality of data produced by genomic analyses, and as analysis techniques become more sophisticated, DNA quality becomes even more important. For example, long-read sequencing enables the detection of variants that are often difficult to resolve with short reads, but it requires high-quality, high-molecular-weight input DNA to be successful.
DNA integrity must be maintained from the moment of sample collection to when the sample is processed in the lab to produce the best results. This can be particularly challenging with large genetic studies where DNA samples are collected from donors at home. Samples may be in transit for several days and exposed to wide temperature fluctuations before they reach the lab. DNA samples are particularly vulnerable to degradation in hotter, humid conditions.
The DNA integrity of a sample can be reduced during shipping and storage via several mechanisms :
- Enzymes (e.g. nucleases) and chemicals present in samples may degrade DNA
- Repeated freeze-thaw cycles, particularly if samples are exposed to low temperatures during shipping, may shear long pieces of DNA into shorter fragments
- Microbes present in samples may grow, adding to the proportion of microbial DNA present, and also producing chemicals and enzymes that may damage target DNA.
Microbial DNA present in samples can be a particular problem for microbiome analysis. During transport and storage, some microorganisms in the sample may continue to grow at the expense of others, meaning that the sample is no longer representative of the original community.
Traditionally, freezing was the standard method for DNA preservation, but freezing presents logistical challenges, especially in field settings or when samples need to be transported over long distances. Freezing requires a lot of energy, the cold chain must be maintained, and the weight of the ice used to keep samples frozen adds to shipping costs. If the cold chain fails during shipment or storage and the sample is subjected to freeze-thaw cycles, then this can cause DNA shearing.
Fortunately, alternative techniques are available that can maintain DNA integrity without the need for freezing. In this article, we’ll explore some of the methods of maintaining DNA integrity within saliva, swabs, and stool samples.
DNA Preservation using Desiccation
Desiccation, or drying, is a simple method for DNA preservation that works well for swab samples. Silica gel or similar desiccants are used to absorb moisture from the environment surrounding the DNA sample. By removing water from the sample, desiccation inhibits the activity of nucleases and other enzymes that could degrade DNA. Desiccation is particularly useful for preserving DNA in field settings where access to freezers may be limited.
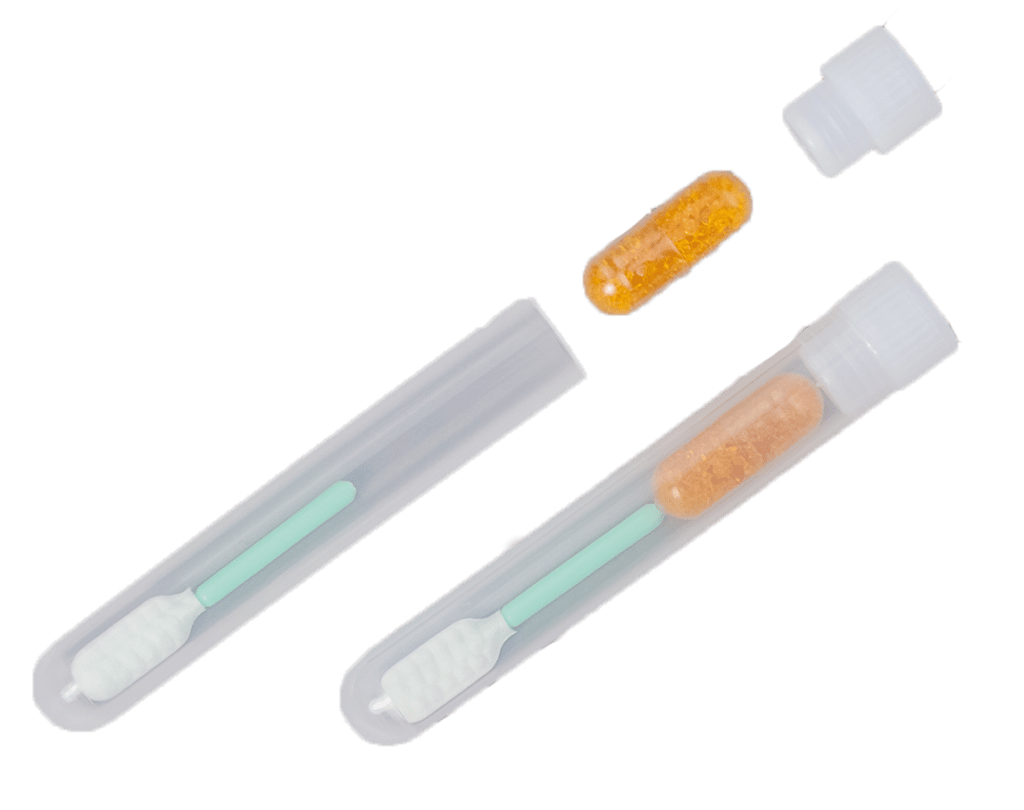
Isohelix SGC Dri-Capsules are a fast and simple way of stabilizing buccal swab samples. A silica gel capsule is placed in the collection tube sitting on top of the swab shaft, maintaining DNA integrity for up to three years.[i]
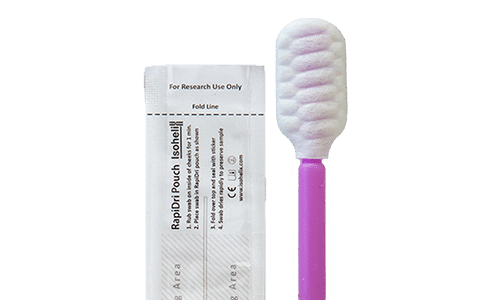
Alternatively, the Rapi-Dri swab kit from Isohelix contains an easy to use buccal swab and a quick-drying pouch with a unique matrix that rapidly stabilizes samples by removing water. The pouch then acts as a sealed shipping unit for sample transport. Sample integrity can be maintained even if samples are subjected to particularly hot and humid environments. [ii]
Stabilizing DNA using Chemical Stabilization Reagents
Chemical stabilization reagents prevent DNA degradation within saliva, swabs, and stool samples, even at ambient temperatures. Many commercially available reagents contain guanidine thiocyanate, which denatures proteins and inactivates nucleases. Although these reagents are easy to use, guanidine thiocyanate is hazardous, and so care must be taken when handling reagents containing this chemical.
Isohelix stabilization reagents do not contain hazardous reagents, so donors can use them to collect samples at home and post them to the lab. DNA in samples is immediately stabilized upon contact with the reagent. Depending on the sample type there are a range of different reagents and kit formats.
Stabilization of DNA from Buccal Cells
Swabs are a straightforward method of collecting donor DNA.
For swabs that have been used to collect buccal cells, the collection tubes in the Isohelix BuccalFix DNA Stabilisation and lysis kit contain a buffer that has been specifically formulated to allow long term storage of swab samples at room temperature, enabling the subsequent isolation of high DNA yields and purity from the stabilized swabs.
Stabilization of DNA in Saliva Samples
Saliva samples can also be collected using swabs. To maintain DNA integrity with saliva samples, Isohelix SaliFix™ swab collectors are recommended. The kits contain SaliFix™ SwabCatcher tubes prefilled with SaliFix™ buffer that is optimized to work with saliva swab samples
For larger volumes of saliva, e.g. 1-3ml, GeneFix DNA/RNA collector tubes are pre-filled with a stabilization reagent that can stabilize DNA at room temperature for over five years.
If, however, you are interested in microbial DNA rather than human DNA, Isohelix has developed a new chemistry designed to maximize the collection and preservation of microbial DNA from human saliva samples. The reagent is included in the GeneFix Microbiome DNA Collector Kit, and can be used to provide a snapshot of the microbiome at the point of collection, stabilizing samples for over 12 months.
Stabilization of DNA from Stool Samples
Studies investigating individual gut microbiomes require the purification of microbial DNA from faecal samples. It is important that these samples are collected and stabilised correctly to ensure that the microbiome at the point of collection is analysed, and results are not biased by sample handling after collection.
Isohelix swabs, combined with StoolFix stabilization buffer, can be effectively used to collect and preserve microbial DNA from faecal samples. Samples are collected by brushing the stool lightly with each face of the swab and are stable at room temperature for up to two months.
Conclusion
Isohelix offers a range of DNA and RNA stabilization solutions that maintain nucleic acid integrity at room temperature for buccal cells, saliva, and stool samples. All stabilization products are optimised for use with Isohelix DNA extraction kits.
[i] Dri-Capsule_3_Year_Study.pdf (isohelix.com)
[ii] RapiDri-Genotyping-Heat-App-Note-ver-4-020721.pdf (isohelix.com)



 Email Us
Email Us